GRACE - Gravimetric Mass Balance
Description
The European Space Agency's (ESA) Climate Change Initiative (CCI) aims at providing reliable, long-term, satellite-based data products allowing to better understand and manage climate change. Data products are generated for key variables (Essential Climate Variables) of the climate system, one of them being the Antarctic Ice Sheet (AIS). The Antarctic Ice Sheet CCI project uses various sensors to address different parameters of the AIS (Read more), including ice mass balance.
Ice sheet mass balance, that is, the change in ice mass over time, is determined using the US-German satellite gravimetry mission GRACE (Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment). GRACE provides the only space method that is directly sensitive to mass changes. The mission consists of two satellites flying at ~500 km in a distance of ~200 km. The details of the Earth’s gravity field affect the positions and speeds of the two satellites and thereby entail variations of the distance between the two satellites. This distance is measured with a micrometer precision. Based on the GRACE measurements, global solutions of the Earth's time varying gravity field are provided by different processing centres. Observed changes of the Earth's gravity field allow to infer changes in mass at a spatial resolution of 200-500 km.
References
1. ESA - gravimetric Mass Balance (GMB) product
2. GMB Gridded product download page
3. Groh, A., & Horwath, M. (2016). The method of tailored sensitivity kernels for GRACE mass change estimates. Geophysical Research Abstracts, 18, EGU2016-12065Available here
Figure
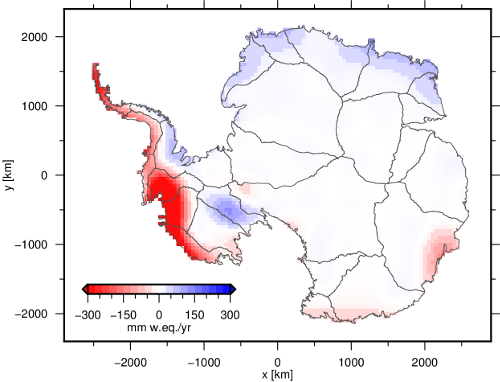
Figure 1: Spatial pattern of the linear mass change rate during the period 2002-08 - 2016-07, expressed in millimetre water equivalent per year (mm w.eq./yr or kg/m2/yr).. University of Dresden